What is osteoarthritis?
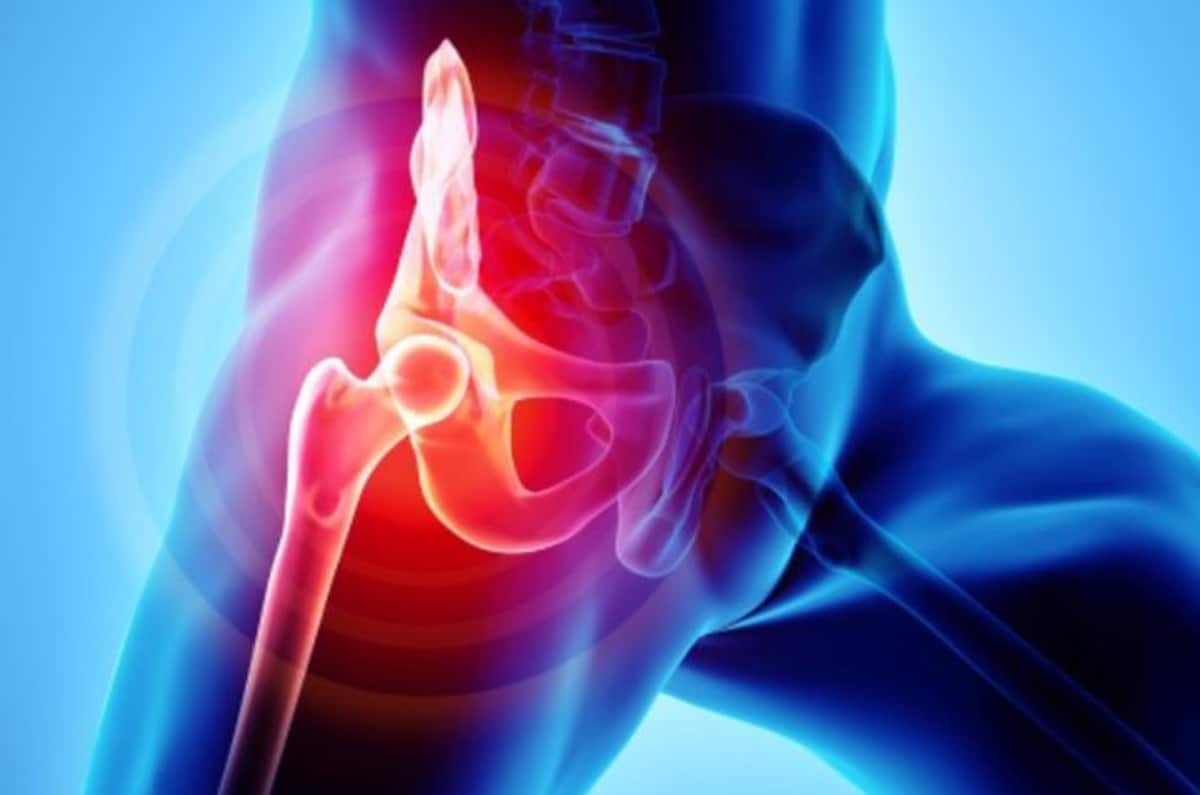
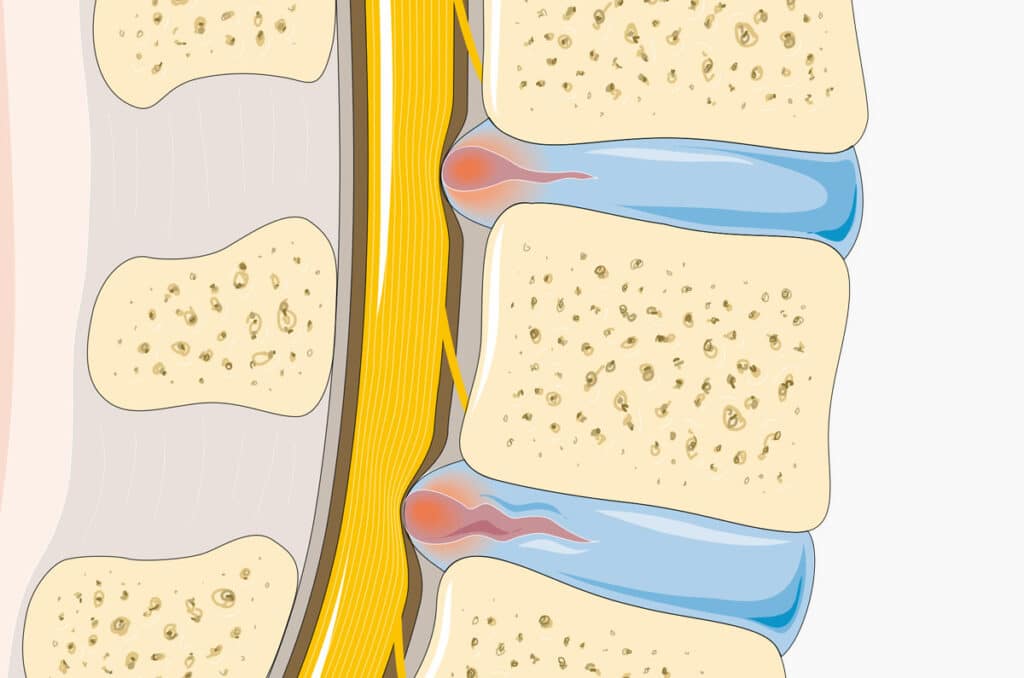
This is a condition in which one has degeneration of the hyaline cartilage- the most abundant cartilage in the body. This lines the joints and functions to both shock-absorb as well as to manufacture synovial fluid which lubricates the joints and permits smooth movement. OA can affect any joint, but mainly the hands, knees, hips and facet joints in the spine.
Many people with severe OA live without any symptoms, though they usually have joint stiffness which they may not even be aware of. Those who suffer from the joints feel pain as well as joint stiffness. With time, the range of motion becomes more limited and then more and more stress is applied to neighbouring joints and other structures with more weight-bearing on the opposite side, so that other joints become more susceptible to develop OA as well. Obesity is a very significant risk factor, not only for developing OA, but for failing to respond to any treatment given for this condition, whether injections of any type or joint replacement. Steroid injections result in more joint damage than benefit.
Until recently, there was no alternative for the treatment of OA; we could only treat the symptoms. Joint replacement was the last option though carries risks and requires a long rehabilitation process. Hip joint replacement, for example, carries very few risks and high success rates, however most of them are much more complicated to replace and carry many more risks with lower success rates (including the knee).
- Fortunately, there has been much research in the field of regenerative medicine. This relatively new field has opened up new options, such as injection of platelet-rich plasma, or platelet-rich fibrinogen and stem cell injection. These treatments are capable of not only postponing the operation but may make the operation redundant in many cases. They are recommended especially when treating joints that are more complicated to replace and in patients who carry surgical risks due to underlying medical illnesses.
- In cases where the cartilage degeneration is very severe or has not responded to any treatment (including joint replacement), one can treat the pain itself using various nerve blocks; if these work temporarily then one can proceed to using radiofrequency or cryoablation, whereby the nerves are either burned or frozen, respectively. Patients who suffer from neuropathic complications may benefit from nerve hydrodissection.